Is your business or blog GDPR complaint?
If you answer “No” or, “What’s GDPR?”
Then, you should read this post very carefully!
In the last few days the online business space has been in a frenzy as online entrepreneurs and webmasters hustled to beat the 25th of May, 2018 deadline of being GDPR compliant. I’m sure that you must have received one of those emails telling you that their privacy policy have been updated!
So, what is GDPR compliance and what’s its implication for your online business?
If you are like me, then you must be asking these questions like right now. When I first heard about the GDPR I didn’t rush into updating my Privacy Policy instead I sought out different experts and also tried reading the GDPR document. But it wasn’t an easy task because the document is highly complex and simply unreadable.
I also found some articles and blog posts on Google but most of them had little to offer as they were mostly written to promote some product or the other. Many others were just a few thoughts on the GDPR document.
However, after much research and asking around, I was able to glimpse some insight into its meaning after which I reworked and updated my site’s Privacy Policy.
You can read the updated Privacy Policy here. It’s important that you read because it is the binding document on this site right now.
In this post, I want to share with you a few things on the GDPR and also give you a few tips on how you can easily stay complaint.
Related: Google’s New Privacy Policy: How Much Of User’s Rights Is Being Violated?
DISCLAIMER: I am not a lawyer neither am I in any away an expert on legal matters. What I have done here is to make this complex topic understandable and actionable for you, within my own understanding of the topic. This article is for informational purposes only. I recommend that you consult your legal advisor to determine your own GDPR needs.
That being said, let’s get started…

Part 1: An Overview of the GDPR
What is GDPR?
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation and it is a new privacy regulation created by the EU to protect the privacy of all individuals within the European Union. Its focus is to give people more control over their personal data. This new regulation replaces the Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC and it is designed to harmonize data privacy laws across Europe.
While the regulation actually applies to businesses in the EU it however has effect on businesses outside the EU as long as they collect or process personal data of individuals residing in the EU.
This is where your blog or small online business is affected.
Of course, as an online business your operations are worldwide and persons from the EU do visit your website, blog or social media pages – except of course, if you’re blocking traffic from that part of the world!
Another very critical issue with this regulation is that though the deadline to be compliant was 25th May, 2018 it is also retroactive.
This means, if you have customers’ or subscribers’ data you’re storing or using even if these were collected before May 25th, 2018, you must ensure that you are also compliant on those too!
This is really serious and it will interest you to know that just a few day after the deadline Google, Facebook, Apple, Amazon, LinkedIn and others have been hit with serious GDPR complaints.
While these privacy activities may be targeting these giants for now, no one knows what they will be doing next. Remember that wise saying, a stitch in time saves nine!
If that does not give you some reason to be complaint, then this should…
The Penalties for Non-Complaint with GDPR
When I first noticed the panic this new regulation caused among online marketers I knew this was something special. And so, I was not surprised therefore when I discovered that most of the panic was actually because of the penalty – €20 million or 4% of your world-wide annual revenue, whichever is higher.
With that do you still want me to remind you at this point that you should take every step necessary to stay compliant?

What Is Personal Data?
It is important you understand the definition of personal data according to the European Commission. This will help you better understand what you need to do to stay complaint with this regulation.
According to the European Commission,
“Personal data is any information relating to an individual (the data subject), whether it relates to his or her private, professional or public life. It can be anything from a name, a home address, a photo, an email address, bank details, posts on social media networking website, medical information, or a computer’s IP address.”
From the above definition (note that even a computer’s IP address is considered as personal data) it is clear that if you own a website or a blog, if you’re an online marketer, if you market on social media, if you use any form of tags for re-targeting customers…
… As long as you capture and record user data of any form, you need to be GDPR compliant!
It will interest you to know that websites and blogs, especially those that run on the WordPress platform, collect personal data in different ways. Some of these ways include:
- Through registered users
- Through comments posted on your blog
- Through the use of contact forms on your site or blog
- Through Google Analytics and other traffic monitoring software
- Through email subscriptions
- Through WordPress plugins
The Rights of Data Subjects Under the GDPR

Now, while you might be tempted to simply update your Privacy Policy and think that will do the trick, the truth is, that’s just the beginning.
The crux of the matter is the rights of the individual under this new regulation. It’s expected that if you receive any request related to any of these rights, you should respond within 30 days. So, it’s important that you know what these rights are and how to go about protecting them.
To get the full details about these rights you may want to check out the official GDPR site referenced above. However, for the purpose of this post, here’s a brief summary of the rights of the individual under the regulation.
1. The Right To Be Informed
The individual is expected to know what type of data you collect about him or her and how it is to be used. You should provide clear and concise information why this data is being collected, how it will be saved, for how long, who has access to it and who is the data controller.
2. The Right Of Access
Beyond knowing how you store their personal data, the individual also has the right of access to that data whenever they wish. So, a subscriber to your email list or a user of your website can demand to have access to the data you have saved about him or her and you are obligated to provide such data.
3. The Right To Rectify Saved Data
The individual also has the right to have their inaccurate or incomplete data that is saved by you to be updated or rectified. Whenever, you or your data controller receives such a request you are obligated to take the necessary steps to have the data updated as requested.
4. The Right To Restrict
The individual also has the right to restrict the use of his or her data. In this case, you may record such data but not use same for any purpose.
5. The Right To Port Data
If the individual so wish he or she may request their saved data in machine readable or human readable formats. They are free to use this data for whatever purpose they so wish.
6. The Right To Erasure
The individual also has the right to withdraw their consent and request that their saved data be erased completely.
7. The Right To Object
The individual have the right to object the use of their data in a certain way. It is therefore important that you inform the user ahead of how their data is to be processed.
8. The Right Not To Be Subject To Automated Decision-Making
Where the data you saved about a user is to be used for some form of automated decision-making that will affect them legally or otherwise the individual has the right to opt out of such processes.
While all of these sound complex it is important that you understand them so you can stay complaint.
What Does GDPR Mean for Your Business?
From the above, every business owner, blogger, web master, internet marketer, etc. (as long as you collect and process personal data of users and customers) has the following responsibilities:
- Provide users your identity and inform them the type of information you collect about them, how and why you collect it, what you do with it, how long you store it, and who else have access to it
- Obtain clear and explicit consent from the user when you collect their data
- Give access to the user when they request such
- Delete any use’s data whenever such a request is made and show proof that you have done this
- Where there is any form of data breach, inform the users within 72 hours.
The question now is how do you ensure that you are complaint with all of these? This is what we want to look at next.
Part 2: GDPR Compliance Checklist
Steps to Staying Complaint with GDPR
Let me repeat once again that the GDPR document is complex. The following is simply a basic guide of what you can do to be complaint.
Step 1: Update the Legal Pages of Your Website or Blog
These basically include your terms of use and privacy policy pages.
The terms of use or terms and conditions page on your site are basically the place where you state the rules that bind the user to your business. The privacy policy on the other hand deals with what type of data about your users and customers that you collect and process.
You will need to update these pages to include relevant information about GDPR compliance. Most of this will be on your privacy policy, since it is the document that deals primarily with consumer data on your site or blog.
Your updated privacy policy should specifically state who you are (which includes your name or organization name, address, contact information, etc), what personal data you collect, why you collect the data, how long you plan to retain the data, who else you share it with, how customers can download their data whenever they so wish, how they can delete or ask their data to be deleted, contact Information of your Data Protection Officer (which could just be your email address except you have a dedicated Data Protection Officer).
All of these should be clearly stated on your privacy policy page.
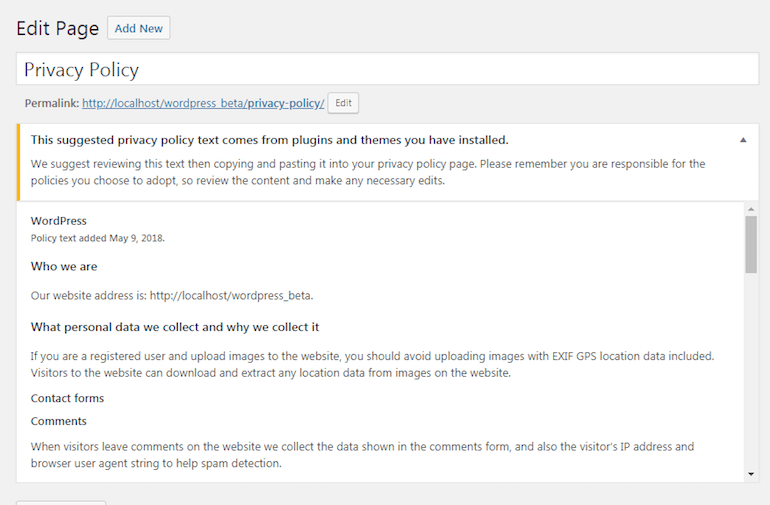
If you use WordPress for your site/blog then you will be glad to know that the latest version has a new feature that allows you to easily create your blog’s privacy policy.

To use this feature:
(a) Go to Settings -> Privacy

(b) Create a new page or choose your already existing privacy policy page to set it.

If you’re creating a new page, WordPress will populate the new page with the basic information that you need to have on your privacy policy. However, before publishing it you will need to review it, adding or removing data to agree with what you expect to have on your privacy policy.
Step 2: Obtain Explicit Consent of the User before Collecting Their Personal Data
Since you’re required to get the consent of the user before you can process their data you should do everything possible to ensure that this is obtained. Look into the areas from which you collect data of users. This will include places like blog comments, contact forms, newsletter subscriptions, etc. Make sure you have the explicit consent of the user before capturing their information.
The easiest way to do this is to put a checkbox on all the places from which you collect data for the user to provide their consent. It’s important that you’re specific of what consent you’re asking for and include a link to your privacy policy. Also it’s important that you don’t pre-check the checkboxes.
Again the latest version of WordPress already has this feature for comments.

Step 3: Clean Up Your Existing Email List
Since GDPR is retroactive you will need to clean up your existing email list to ensure that you only have subscribers who has given their consent. One way to do this is to send re-engagement emails so that your EU subscribers can re-optin to your list. Ensure that you clearly explain how you’d use the subscribers’ data and what content you will be sending them.
Step 4: Create a System for Data Subjects to Request Access to Their Data
GDPR requires you to allow users access to their data. It is not enough to state this on your privacy policy. You should also have in place a way for them to easily access the data when they so desire.
There are a number of ways you can do this. For example, if a user request to have access to the personal data you’re processing about them, you can take a screenshot of the customer record or you can export the contact details of the user in a CSV file and then send it to them.
This is another thing that the latest version of WordPress has made easy for you also. There are new tools for users to view their data, and even request deletion of their data. You can access these new tools by going to Tools.

Here’s the process of using these tools:
- User requests to view or delete their data
- You go to Tools and then to the Export or Erase Personal Data Setting
- You enter the user’s email id, and click “send request”
- This sends a confirmation link for the user to confirm their request
- Once the user confirm the request you can then send them a downloadable file containing the requested data with the click of a button
- Once this file has been sent it will be deleted after 72 hours for security purposes
- If the request is for deletion, then as soon as the user confirms the request you can delete the data.
Conclusion – More Resources
There you have it, my simple guide to help you stay GDPR compliant. Please understand that, as I have mentioned earlier this is a complex topic. There’s so much that I have not touched on in this post. To dig deeper feel free to browse these resources:
- General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) full text
- Frequently Asked Questions and Answers regarding GDPR
- A guideline on identifying a Data Protection Officer
Again note that violating the GDPR comes with a heavy fine of 20 million Euros or 4% of your revenues, whichever is higher. If however you take the above necessary steps, you’ll not have to worry much.
I do hope that this has helped in any way. If so, then show some love by sharing the post with your friends on your favorite social media!
Feel free also to share your thoughts on the GDPR in the comments below.
Loved What You've Just Read?
Then join 3,047 other HAPPY Subscribers and get FREE updatesin your email inbox starting now!
Enter Your Details to Receive FREE Updates
We hate spam and your info. is safe!
GDPR Compliance – A Practical Guide for Bloggers and Small Business Owners was first posted on June 5, 2018 at 9:08 am.
©2014 "The Web Income Journal!". Use of this feed is for personal non-commercial use only. If you are not reading this article in your feed reader, then the site is guilty of copyright infringement. Please Click here to contact me.


















